Babesiosis: symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
What is babesiosis, and how does it manifest?
Babesiosis is a severe parasitic disease transmitted to dogs by biting an infected tick. The parasite Babesia canis attaches itself to the dog’s red blood cells, destroying them and leading to a number of health problems.
How does babesiosis manifest itself in dogs?
Symptoms of babesiosis may appear days or even weeks after the tick bite and may include:
- Fever: An increase in body temperature that may be difficult to notice.
- Lethargy: The dog appears tired, lacks energy and has little desire to play or walk.
- Loss of appetite: The animal refuses food or has a reduced appetite.
- Weakness: The dog appears weak and has difficulty walking or standing.
- Dark urine (reddish or brown): A sign of red cell destruction.
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and mucous membranes): Another sign of red cell destruction.
- Breathing difficulties: Due to anemia (decreased number of red blood cells).
Babesiosis – Diagnosis
Although we can identify certain symptoms of babesiosis in dogs, we recommend, as always, a visit to a specialized office.
A veterinarian can diagnose babesiosis by:
- Clinical signs: The doctor will examine the animal and consider the medical history and lifestyle.
- Blood tests: Specific tests can be performed to detect the presence of the Babesia canis parasite or antibodies against it.
- Other tests: In some cases, additional tests, such as X-rays or ultrasounds, may be needed to evaluate possible damage to the liver or spleen.
How can I treat babesiosis?
Babesiosis is a serious disease that requires immediate treatment with specific drugs in the veterinary office. The duration of treatment varies depending on the disease’s severity and the animal’s general health.
In most cases, the fight against babesiosis involves a specific anti-babesiosis treatment scheme and a supportive treatment. The quadruped will be given antibiotics and vitamins against the disease through infusion solutions.
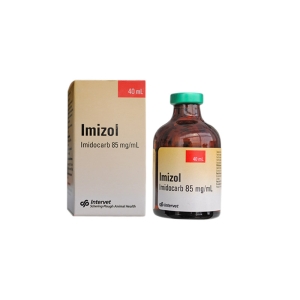
Imidazole is an effective drug used in the treatment of babesiosis in dogs. The active substance in Imizol is imidocarb, which acts on the infection with the parasites responsible for babesiosis. Imizol is often used in combination with other treatments and supportive therapies to improve the chances of recovery of the dog affected by this disease.
It is essential to administer Imizole under the supervision of a qualified veterinarian as it may be associated with adverse reactions and requires appropriate dosing and monitoring to ensure the effectiveness and safety of the treatment.
How can I protect my dog from babesiosis?
Prevention is critical to protecting your furry friend from babesiosis. Here are some steps you can take:
- Tick Control: Use both internal and external deworming products recommended by your veterinarian to prevent tick infestation.
- Regular examinations: Carefully examine the animal’s fur after each walk to detect and remove ticks.
- Avoiding risk areas: Avoid walking in areas with abundant vegetation, where ticks are more common.
The prognosis of babesiosis
With early diagnosis and proper treatment, most dogs infected with babesiosis fully recover.
Remember: Babesiosis can be a serious disease, but it’s important not to panic. With a preventative approach and careful monitoring, you can protect your furry friend and enjoy summers full of play and adventure!